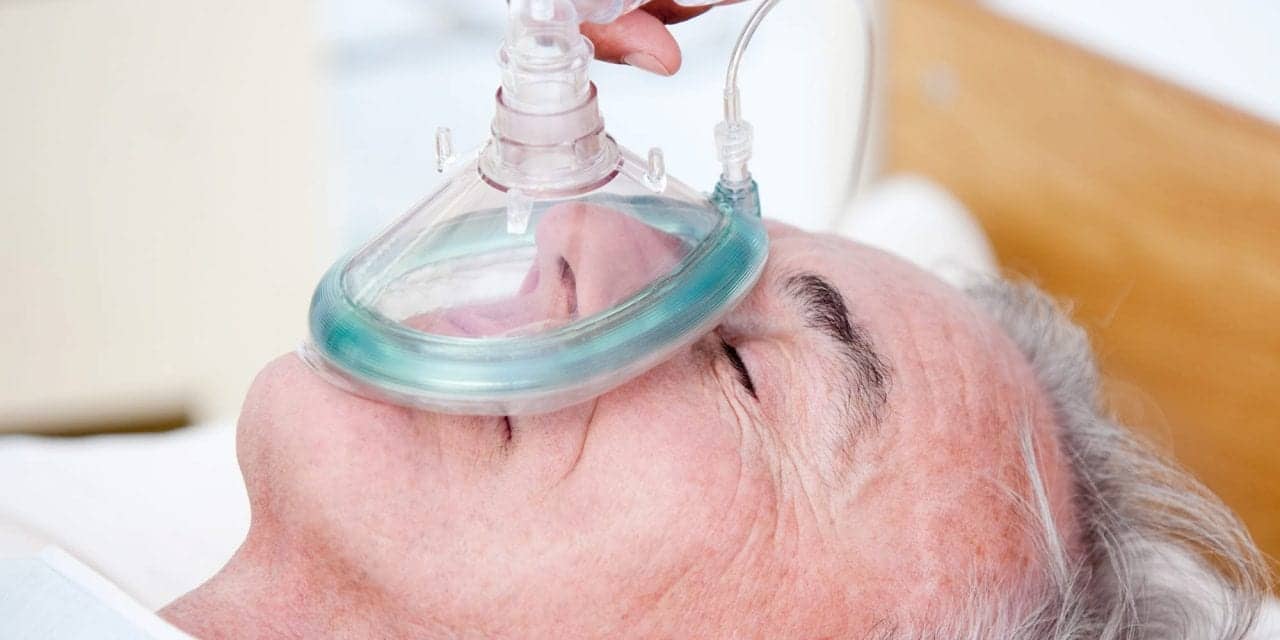
does oxygen prolong life at end of life
Reversal of hypoxemia in some cases will alleviate dyspnea. Each experience is different at the end of life.
![]()
How Hospice Helps Copd Patients Inspiration Hospice
3 Of 200 subjects 99 received NIV and 101 oxygen.

. 1011 In a survey sent to 648 palliative care specialists 70 of them responded that they had ordered palliative oxygen if the patient was dyspneic. Its common to wonder what happens when someone is dying. If it makes a difference - my mom had not been eating much for quite some time and not at all for a bit.
For patients at the very end of life it can unnecessarily prolong the dying process. Others remain physically strong while cognitive function declines. Theres some point at which that the oxygen level gets so low that its no longer compatible with life.
Circulation is slowed breathing is slowed so oxygen exchange between the lungs and the blood is slowed. If the patients respiratory status deteriorates intubation and ventilation are initiated. In end-of-life care mechanical ventilation is applied not to prolong the lives of patients but to reduce their anxiety and to allow them to sleep better and eat more comfortably.
This equipment does the work of the body organ such as. Oxygen is commonly prescribed for lung cancer patients with advancing disease. A machine to help with breathing.
In most situations it does not prolong life and it is even questionable if it can ease the air hunger that is part of the dying process. It states that the physical body is so compromised due to decreased circulation and lung congestion that there is no effect. It may prolong dying.
Barnes et al 2016. For some older adults at the end of life the body weakens while the mind stays clear. Liative care coordinators the use of oxygen in end-of-life care was questioned by cited authors and growing evidence suggests that oxygen use may not always be indicated 3 and may be unbeneficial 4 and unnecessary 5 at the end of life.
Supplemental oxygen does not have a role in end-of-life palliation. In the days to hours before death when our body is shutting down the heart is unable to pump the blood normally through the body. Oxygen is useful initially if oxygen saturation is less than 90 but it might prolong the dying process in patients who are about to.
If youre providing supplemental oxygen that might just take longer said Dr. A more recent study out of the University of Bologna Italy examined the use of opiates in combination with non-invasive ventilation NIV versus oxygen therapy in patients with end-stage cancer. What is normal oxygen level for elderly.
Prolong survival 10 11. While some patients may derive symptomat. Goals of NPPV at the end of life NPPV is used in 3 general circumstances in patients close to death all of which are likely to be encountered by palliative specialists 1.
Oxygen canwill depending upon the circumstances prolong life. There are no specific best practice guidelines on the use of oxygen at the end of life. At some point the oxygen level gets so low its no longer compatible with life.
Lab mice have gigantic telomeres much longer than humans. Supplemental oxygen is frequently prescribed for patients in palliative care to manage their dyspnea at the end of life even if they are not hypoxemic. If the patient appears feverish and has a high temperature acetaminophen suppositories are often prescribed.
Death can come suddenly or a person may linger in a near-death state for days weeks or even months. Does oxygen prolong life at end of life. Thirty percent of the ordering physicians.
So will hydration warmth and other basic necessities. For patients at the very end of life it can unnecessarily prolong the dying process. Pneumonia is a common end-of-life complication in many progressive chronic conditions including dementia malignancy and neurodegenerative respiratory and rheumatologic.
A tube into your stomach to provide food nasogastric or gastrostomy tube A tube into your vein to provide fluids and medicines intravenous IV tube. Does oxygen prolong life at end of life. As patients respiratory rate starts to fall carbon dioxide is increasing and oxygen levels are decreasing he said.
I see that others here are saying longer - I honestly dont know that much about it. Oxygen is sometimes prescribed for non-hypoxemic patients to relieve dyspnea. A machine to help your kidneys.
It was when my mothers oxygen hit 70 that hospice told me she was transitioning. There is research saying that administering oxygen as the end of life approaches doesnt prolong life or even have any beneficial effects. Thing is the main dogma that youth and longevity are associated with long telomeres and once those get too short after many cell divisions you grow old get cancer and die kind of contradicts what every telomere researcher knows too well.
They said to expect about a week- mom passed early the next morning. Use of any medical intervention - including oxygen - may prolong life somewhat but in general its used to keep a dying person comfortable in their last days and weeks. Approximately 75 of dying patients experience difficulty breathing or dyspnea.
Do dying patients need oxygen. Patients who desire full life-prolonging interventions regardless of prognosis. The first distinction that must be made is between the use of oxygen in unconscious and conscious patients.
Offer oxygen to those with known or clinically suspected symptomatic hypoxemia. This feeling can be scary for patients and those who witness it. Theres some point at which that the oxygen level gets so low that its no longer compatible with life.
Treatments to extend life can include the use of machines. But simple mask- or cannula- delivered oxygen should not considered resuscitative unlike delivery by forced pressure for where you seek to actively inflate the lungs as with a BVM or demand valve. Indications include hypoxemia and dyspnea.
It is not going to prolong life in any meaningful way - rather its used. The normal oxygen saturation level is 97100 OER 1. Oxygen is not recommended for routine use even in the home care setting or in the last days of life.
Another downside of supplemental oxygen. Findings showed NIV to be more effective than oxygen in reducing dyspnea. Forty-three percent of respondents believed that oxygen use at the very end of life affects the timeline of natural death by prolonging the dying process.
In addition some profession-als have postulated that oxygen use at the very end of life may prolong the dying process. Frequently oxygen is continued in patients who are deeply unconscious and in. Opioids are first line treatment.
Do oxygen levels drop when dying. Ninety-six percent of the respondents facilities had a standard comfort care protocol for end-of-life patients that offered oxygen regardless of whether patients had breathlessness or not. Researchers say the problem is reported in 65 percent 70 percent and 90 percent of patients nearing the end of life suffering from heart.

Oxygen Is Nonbeneficial For Most Patients Who Are Near Death Journal Of Pain And Symptom Management

Give Them Comfort Controlling Copd Symptoms At End Of Life

End Of Life Care In Emergency Medicine

End Of Life Signs The Final Days And Hours

Helpful Gardening Hacks That Really Work Organic Recipes Eating Organic Survival Food
Pulling The Plug Icu Culture Key To Life Or Death Decision

Facilitating Anticipatory Prescribing In End Of Life Care The Pharmaceutical Journal

A Commuter Rides A Century Why You Should Clip In On A Bike Bike Riding Benefits Bike Ride Cycling Articles

Pin By Stan Upchurch On Dysautonomia Iron Chef Chef Counting Crows

Too Few Hospitals In Covid Hotspots Are Equipped To Offer Ecmo Shots Health News Npr

Dying Patients Should Be Offered Water In Their Final Hours New Guidelines Say The Independent The Independent

What Is A Death Rattle How Long After The Death Rattle
Death Natural Or Assisted A Guide To Medical End Of Life Issues

Oxygen Is Nonbeneficial For Most Patients Who Are Near Death Journal Of Pain And Symptom Management

5 Physical Signs Of Impending Death When End Of Life Is Near
.png)
End Of Life With Pulmonary Fibrosis Action For Pulmonary Fibrosis